Oceanic organisms live in a hypertonic environments.
If you’re searching for oceanic organisms live in a hypertonic environments pictures information linked to the oceanic organisms live in a hypertonic environments interest, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our website always provides you with hints for viewing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video content and images that fit your interests.
 Chapter 12 Marine Life And The Marine Environment From slidetodoc.com
Chapter 12 Marine Life And The Marine Environment From slidetodoc.com
Identify symbiotic relationships in which both organisms benefit. Instead of being hydrated by the water the solute -dense ocean water will pull water from the body to balance the difference in osmolarity. These organisms are called Osmoregulators. The ocean is made of salt water and is a hypertonic solution compared to cells.
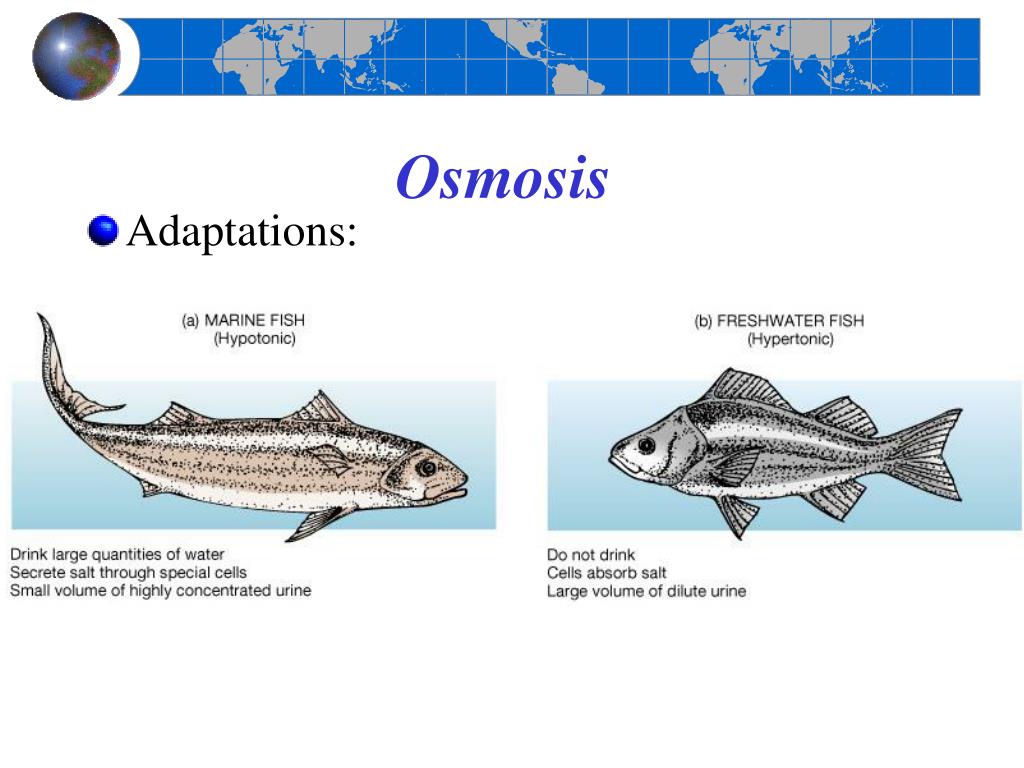
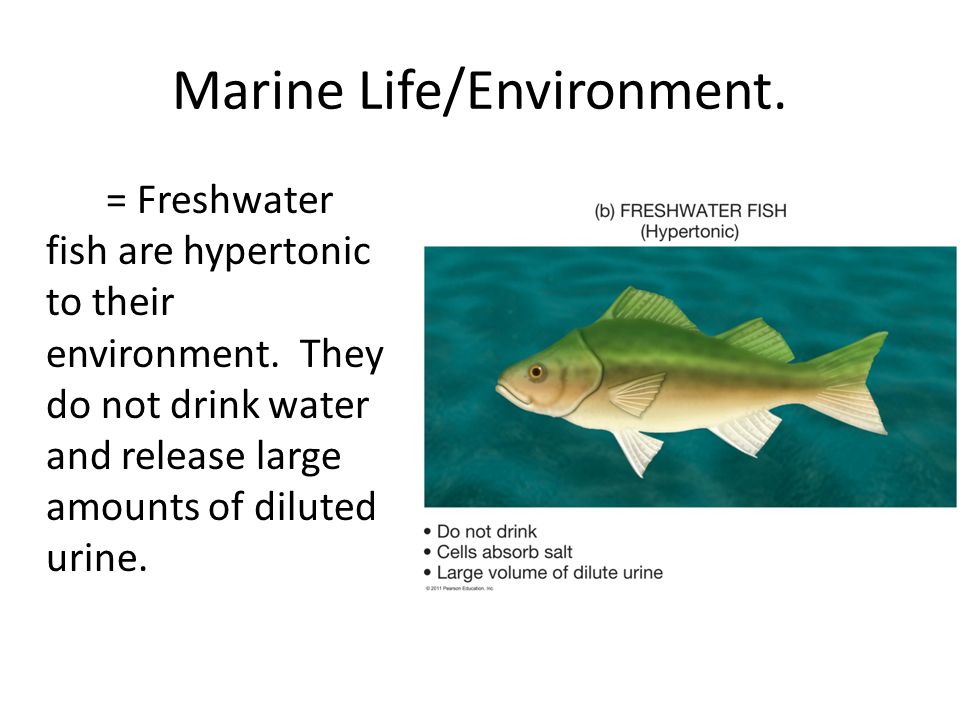
The fluid in the cells of a salt water fish is hypertonic to fresh water ie the concentration of water in the cells of the fish is less than the concentration in fresh water.
Describes organisms living on or in the ocean bottom. Biology questions and answers. Question 19 Oceanic organisms live in aenvironment whereas river organisms live in a environment. Instead of being hydrated by the water the solute -dense ocean water will pull water from the body to balance the difference in osmolarity. Design a new marine organism a predator or prey.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
There are two ways in which aquatic organisms maintain their water balance. The rate of this diffusion depends on the concentration gradient across the membrane. In addition these organisms are normally polyextremophiles being adapted to live in habitats where various physicochemical parameters reach extreme values. Give it adaptations such as specialized body parts or abilities that help it live in the coral reef. These organisms are called Osmoregulators.
Some animals live in extremely hypertonic environments such as sea turtles.
For example many hot springs are acid or alkaline at the same time and usually rich in metal content. Marine worms –nektobenthos swim or crawl through water blank the seafloor ex. Found only in benthic environments d hypertonic with respect to their environment e. Organisms suited to live in a hypertonic environment have to deal with loss of water to the environment that has a lower water concentration.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Organisms suited to live in a hypertonic environment have to deal with loss of water to the environment that has a lower water concentration. Organisms suited to live in a hypertonic environment have to deal with loss of water to the environment that has a lower water concentration. Biology questions and answers. For example many hot springs are acid or alkaline at the same time and usually rich in metal content.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Design a new marine organism a predator or prey. Dinoflagellates also known as pyrophytes peridines or dinoficee are mostly unicellular and flagellate microscopic algae which represent one of the most important marine and freshwater phytoplankton groups with more than 2000. If you place a freshwater turtle in seawater the hypertonic seawater will dehydrate the turtle. Saltwater fish employ is to intake lots of water but excrete the salt.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Create a model or a drawing of your organism. Some animals live in extremely hypertonic environments such as sea turtles. Dinoflagellates also known as pyrophytes peridines or dinoficee are mostly unicellular and flagellate microscopic algae which represent one of the most important marine and freshwater phytoplankton groups with more than 2000. Fish that live in salty marine waters absorb most of the water they take in and expend energy to excrete the excess salt through their kidneys and gills.
If you put a freshwater turtle in seawater the hypertonic seawater will dehydrate the turtle. Hypertonic and Hypotonic Environments Salts and sugars in solution will diffuse away from areas of high concentration into the surrounding solution. Some animals live in extremely hypertonic environments such as sea turtles. The fluid in the cells of a salt water fish is hypertonic to fresh water ie the concentration of water in the cells of the fish is less than the concentration in fresh water.
Sea stars anenomes –infauna live buried in blank ex.
Sea stars anenomes –infauna live buried in blank ex. SALMON and other so-called anadromous fish species spend portions of their lives in both fresh and saltwater. Describes organisms living on or in the ocean bottom. Organisms such as goldfish that can tolerate only a relatively. Some animals live in extremely hypertonic environments such as sea turtles.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
The rate of this diffusion depends on the concentration gradient across the membrane. Molecules of soluble substances such as nutrients move through water from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration until the distribution of the substance is uniform. Organisms suited to live in a hypertonic environment have to deal with loss of water to the environment that has a lower water concentration. Instead of being hydrated by water the solute-rich ocean water will draw water out of the body to balance the difference in osmolarity. Question 19 Oceanic organisms live in aenvironment whereas river organisms live in a environment.
Saltwater fish employ is to intake lots of water but excrete the salt. If you place a freshwater turtle in seawater the hypertonic seawater will dehydrate the turtle. For example many hot springs are acid or alkaline at the same time and usually rich in metal content. Identify and describe adaptations that help specific ocean organisms survive.
Sea turtles for example live in a much more hypertonic solution compared to freshwater turtles.
Aquatic organisms that live in hypertonic or hypotonic environments have adaptations for dealing with water balance maintenance. One way is to control internal osmolality within their cells independent of its environment. Fish osmoregulate through their gills kidneys and intestines. IC isotonic hypotonic hypertonic.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Organisms suited to live in a hypertonic environment have to deal with loss of water to the environment that has a lower water concentration. Design a new marine organism a predator or prey. Organisms suited to live in a hypertonic environment have to deal with loss of water to the environment that has a lower water concentration. Water also diffuses away from areas of high free water concentration into areas of.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Identify and describe adaptations that help specific ocean organisms survive. The ocean is made of salt water and is a hypertonic solution compared to cells. Some animals live in extremely hypertonic environments such as sea turtles. Instead of being hydrated by the water the solute-dense ocean water will pull water from the body to balance the difference in osmolarity.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The deep ocean is generally cold oligotrophic very low nutrient content and exposed to high pressure. A wandering albatross spends months at a time flying or floating on the open ocean far from any source of fresh water. Organisms living in seawater must have a means of preventing the loss of water from the body to the highly saline and potentially hypertonic environment. For example many hot springs are acid or alkaline at the same time and usually rich in metal content.
Identify symbiotic relationships in which both organisms benefit.
Found only in benthic environments d hypertonic with respect to their environment e. The rate of this diffusion depends on the concentration gradient across the membrane. Sea turtles for example live in a much more hypertonic solution compared to freshwater turtles. If you put a freshwater turtle in seawater the hypertonic seawater will dehydrate the turtle. Crabs –benthos are most abundant in blank water.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Saltwater fish employ is to intake lots of water but excrete the salt. Question 19 Oceanic organisms live in aenvironment whereas river organisms live in a environment. Some organisms internal salt levels mimic the external thus they are able to survive in a salty environment without water loss. Hypertonic and Hypotonic Environments Salts and sugars in solution will diffuse away from areas of high concentration into the surrounding solution. This is called simple diffusion.
Give it adaptations such as specialized body parts or abilities that help it live in the coral reef.
The rate of this diffusion depends on the concentration gradient across the membrane. Sea turtles for example live in a much more hypertonic solution compared to freshwater turtles. Biology questions and answers. If you place a freshwater turtle in seawater the hypertonic seawater will dehydrate the turtle.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
There are two ways in which aquatic organisms maintain their water balance. The deep ocean is generally cold oligotrophic very low nutrient content and exposed to high pressure. Describes organisms living on or in the ocean bottom. Instead of being hydrated by the water the solute -dense ocean water will pull water from the body to balance the difference in osmolarity.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Persons lost at sea without any fresh water to drink are at risk of severe dehydration because the human body cannot adapt to drinking seawater which is hypertonic in comparison to body fluids. Found only in benthic environments d hypertonic with respect to their environment e. Hypotonic and hypertonic solutions. Fish that live in salty marine waters absorb most of the water they take in and expend energy to excrete the excess salt through their kidneys and gills.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
If you put a freshwater turtle in seawater the hypertonic seawater will dehydrate the turtle. Describes organisms living on or in the ocean bottom. Marine worms –nektobenthos swim or crawl through water blank the seafloor ex. Saltwater fish employ is to intake lots of water but excrete the salt.
So albatrosses have evolved a way to drink seawater which is too salty.
Instead of being hydrated by water the solute-rich ocean water will draw water out of the body to balance the difference in osmolarity. These organisms are called Osmoregulators. A simple solution no pun intended that eg. Instead of being hydrated by water the solute-rich ocean water will draw water out of the body to balance the difference in osmolarity. The deep ocean is generally cold oligotrophic very low nutrient content and exposed to high pressure.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Crabs –benthos are most abundant in blank water. If you place a freshwater turtle in seawater the hypertonic seawater will dehydrate the turtle. Saltwater fish employ is to intake lots of water but excrete the salt. Fish osmoregulate through their gills kidneys and intestines. Describes organisms living on or in the ocean bottom.
It is generally less dense than the ocean water surrounding it so animals naturally float.
The deep ocean is generally cold oligotrophic very low nutrient content and exposed to high pressure. Some animals live in extremely hypertonic environments such as sea turtles. This is called simple diffusion. Some have gills and renal.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The fluid in the cells of a salt water fish is hypertonic to fresh water ie the concentration of water in the cells of the fish is less than the concentration in fresh water. One way is to control internal osmolality within their cells independent of its environment. Freshwater fish excrete large amounts of water and retain most of the ions as well as urea. Identify symbiotic relationships in which both organisms benefit. Saltwater fish employ is to intake lots of water but excrete the salt.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Isotonic hypertonic hypotonic hypotonic. Identify and describe adaptations that help specific ocean organisms survive. Isotonic hypertonic hypotonic hypotonic. Dinoflagellates also known as pyrophytes peridines or dinoficee are mostly unicellular and flagellate microscopic algae which represent one of the most important marine and freshwater phytoplankton groups with more than 2000. Fish osmoregulate through their gills kidneys and intestines.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
If you put a freshwater turtle in seawater the hypertonic seawater will dehydrate the turtle. Marine worms –nektobenthos swim or crawl through water blank the seafloor ex. But many animals that live in or near the ocean have evolved ways to pump out the extra salt while keeping their water levels in balance. If you place a freshwater turtle in seawater the hypertonic seawater will dehydrate the turtle. Aquatic organisms that live in hypertonic or hypotonic environments have adaptations for dealing with water balance maintenance.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title oceanic organisms live in a hypertonic environments by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





